CLICK ON CHAPTER

A Guide to Renewable Energy Solutions for Sustainable Living

Nature´s Power
Introduction
Self-sufficient living with alternative energy sources is a cornerstone of sustainable lifestyles, enabling individuals and communities to reduce their dependence on traditional energy grids. By harnessing natural resources like solar, wind, and water, self-sufficient farms and homesteads achieve energy independence while contributing to environmental preservation.
Imagine a life where your home generates its own energy, freeing you from rising utility bills and giving you complete control over your energy needs. These systems not only lower operational costs but also provide resilience during energy crises and support global efforts to combat climate change. By adopting renewable energy solutions, individuals can enjoy a sustainable lifestyle that aligns with ecological responsibility and long-term savings.
This guide explores the evolution of renewable energy technologies and their role in self-sufficient living. Topics include solar power, hydropower, and biogas systems, with practical tools, real-world case studies, and actionable insights to help you achieve energy-efficient solutions tailored to your unique needs.
Historical Development
Self-sufficient living and renewable energy have evolved significantly over the past century, driven by technological advancements, environmental awareness, and the vision of pioneering innovators. The journey from early experiments to modern systems illustrates humanity’s ingenuity and determination to create sustainable solutions for energy independence.
Pioneering figures like Nikola Tesla laid the foundation for understanding energy flow and wireless transmission, pushing the boundaries of what was possible. Viktor Schauberger explored the potential of water vortices for generating power, introducing revolutionary ideas about natural energy systems. Early technologies such as electric coils, magnetism, and copper spirals showcased groundbreaking methods for energy harnessing and management, many of which remain influential in today’s renewable energy designs.
The energy crisis of the 1970s became a turning point, sparking global interest in alternative energy solutions. This period led to the development of solar panels, wind turbines, and small-scale hydropower systems, demonstrating the viability of renewable energy sources. These innovations provided a glimpse of the transformative potential of renewable energy, laying the groundwork for today’s advanced systems that power self-sufficient farms and homesteads.
Modern renewable energy technologies, built upon these historical milestones, empower individuals to reduce reliance on traditional grids while addressing pressing environmental challenges. Understanding this evolution inspires continued innovation and reinforces the importance of adopting sustainable energy practices today.
Solar Power: Installing Photovoltaic Systems for Farms and Homesteads
Solar power is transforming farms and homesteads into self-sufficient energy hubs, offering a sustainable, cost-effective, and scalable solution for energy needs. By harnessing sunlight, photovoltaic (PV) systems provide reliable electricity, reduce dependence on fossil fuels, and lower operational costs. These systems are especially valuable in rural or off-grid areas, where consistent access to affordable energy can drive agricultural productivity and household efficiency.
Advantages of Solar Power
Solar power represents a versatile and renewable energy source, offering farms and homesteads a unique opportunity to achieve energy independence. By investing in solar technology, users can significantly reduce their reliance on traditional grids while also contributing to environmental preservation. The long-term financial and ecological benefits make solar power an essential component of sustainable living.
- Renewable Energy: Solar power is an abundant and infinite resource, reducing reliance on finite non-renewable energy sources.
- Cost Savings: Over time, solar systems lower electricity bills by offsetting energy consumption from the grid.
- Scalability: Systems can be customized for small homesteads or large-scale farms, depending on energy requirements.
- Low Maintenance: Modern PV panels require minimal upkeep, with most systems offering a lifespan of 25-30 years.
- Environmental Benefits: Solar power significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to global sustainability goals.
Steps to Install Photovoltaic Systems
Installing solar panels is a multi-step process that requires careful planning and execution to maximize efficiency. Understanding these steps ensures that your system meets both your energy needs and sustainability goals. Whether you’re planning a small-scale setup or a large farm installation, these principles remain essential.
Site Assessment Evaluating your property’s sunlight exposure is the first critical step in designing an effective solar power system. This process ensures that panels are placed in locations with maximum efficiency, minimizing shading and maximizing energy production.
- Assess factors like shading, roof angle, and orientation to determine optimal panel placement.
- Use professional services or tools like [Solar Monitoring Apps Affiliate Links] to calculate energy production potential.
System Design Tailoring your solar system design to your specific energy needs and budget is crucial for long-term success. Proper design ensures that your setup is efficient, cost-effective, and scalable.
- Decide between grid-tied, off-grid, or hybrid systems based on energy requirements.
- Calculate system size by assessing daily energy consumption and peak usage patterns.
- Use tools like [Solar Panel Kits Affiliate Links] to simplify the design process.
Selecting Components Choosing high-quality components is vital for creating a durable and efficient solar power system. The right equipment not only enhances performance but also ensures longevity and reliability.
- Solar Panels: Opt for monocrystalline panels for higher efficiency or polycrystalline for cost-effectiveness.
- Inverters: Convert DC electricity into AC for farm or household use.
- Batteries: Essential for off-grid or hybrid systems to store excess energy; explore [Battery Storage Solutions Affiliate Links] for reliable options.
Installation Process The installation phase is where planning meets execution. A proper setup ensures system safety, efficiency, and longevity.
- Mount panels on rooftops, ground structures, or tracking systems for optimal efficiency.
- Ensure professional wiring connections to integrate panels, inverters, and storage systems safely.
- Conduct performance tests to verify energy output and system integration.
Monitoring and Maintenance To maximize your investment, regular monitoring and maintenance are essential. This ensures that your system operates at peak performance and identifies potential issues early.
- Clean panels regularly using tools from [Solar Maintenance Kits Affiliate Links] to remove dust and debris.
- Monitor performance with apps or devices like [Solar Monitoring Apps Affiliate Links].
Applications of Solar Power in Agriculture
Solar power is a game-changer for agricultural operations, providing reliable and sustainable energy solutions for various applications. From irrigation to cold storage, solar technology enhances productivity while lowering operational costs.
- Irrigation Systems: Power pumps for reliable and efficient irrigation, even in remote areas.
- Cold Storage: Maintain perishable goods with solar-powered refrigeration systems.
- Lighting: Illuminate barns, greenhouses, and outdoor spaces efficiently.
- Electric Fencing: Secure livestock with solar-powered electric fences.
- Small Machinery: Charge electric tools and small farming equipment, reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
Managing Surplus Energy
Solar power systems often generate more energy than immediately needed. Managing this surplus effectively ensures that none of it goes to waste, adding value to your investment.
- Grid-Tied Systems: Sell surplus energy back to the utility grid, reducing overall energy costs.
- Battery Storage: Store excess energy for nighttime use or cloudy days, ensuring a consistent energy supply.
- Diversification: Utilize surplus power for heating, water pumps, or additional cold storage facilities.
Battery Considerations
Batteries play a critical role in storing energy for later use, especially in off-grid or hybrid solar systems. Understanding their specifications and maintenance needs ensures long-term performance.
- Replacement Timeline: Batteries typically last 5–15 years, depending on type (lithium-ion vs. lead-acid).
- Storage Conditions: Store batteries in cool, dry, and ventilated areas to optimize lifespan.
- Costs and Needs: Battery costs range from $200 to $1,000 per unit, with the number of batteries dependent on system size and energy requirements.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite its many benefits, solar power systems can present challenges. Addressing these proactively ensures a smoother experience and maximizes the value of your investment.
- Initial Costs: Mitigate high upfront expenses with government incentives, tax rebates, and financing options.
- Weather Dependence: Integrate battery storage or hybrid systems to maintain energy output during cloudy or rainy days.
- Land Use: Combine ground-mounted systems with agricultural activities like agrivoltaics to optimize space usage.
Innovations in Solar Power
Advancements in solar technology continue to expand its potential, making it more accessible and effective for diverse applications. These innovations address common challenges and open new possibilities for renewable energy.
- Agrivoltaics: Combining solar panels with crop production optimizes land use and creates beneficial microclimates.
- Floating Solar Farms: Panels installed on water bodies save land and reduce evaporation.
- Smart Systems: Use AI and IoT for real-time performance monitoring and efficiency optimization.
Case Studies
Real-world examples illustrate the transformative potential of solar power, showcasing its effectiveness across different climates and agricultural settings.
- India: Solar-powered irrigation in Gujarat has transformed arid lands into productive farms, reducing dependency on diesel pumps.
- United States: Agrivoltaic systems in California vineyards enhance grape quality while reducing water usage.
- Germany: Dairy farms integrating solar panels with storage systems achieve full energy independence.
Transform Your Farm or Homestead with Solar Power
By harnessing solar power, farms and homesteads can achieve unparalleled energy independence while contributing to environmental sustainability. With tools like [Solar Panel Kits Affiliate Links], [Battery Storage Solutions Affiliate Links], and [Solar Monitoring Apps Affiliate Links], starting your journey toward renewable energy is easier than ever. Explore the possibilities of solar power today and take the first step toward a sustainable and self-sufficient future.
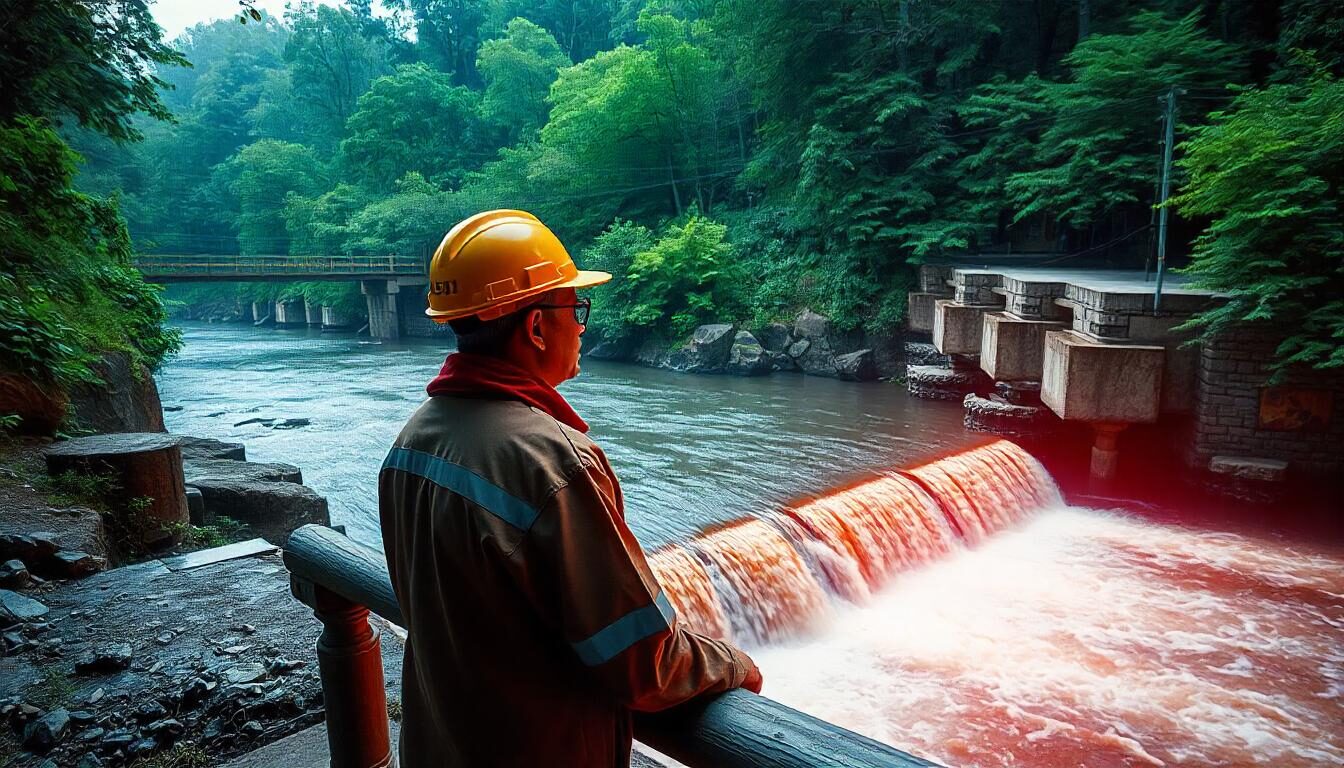
Hydropower: Leveraging Small-Scale Water Turbines for Energy Production
Hydropower is a reliable and efficient renewable energy source that harnesses the power of flowing water to generate electricity. Ideal for farms and homesteads located near streams, rivers, or irrigation channels, small-scale water turbines offer a consistent and sustainable energy solution with minimal environmental impact. These systems not only provide energy independence but also contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation.
How Hydropower Works
Hydropower works by converting the natural kinetic energy of flowing water into electricity, making it one of the most consistent and reliable renewable energy sources. This process leverages the continuous flow of water to power turbines and generate electricity, providing farms and homesteads with a sustainable and uninterrupted energy supply. Understanding how hydropower generates energy is essential for planning an efficient system. By channeling water through turbines, this method converts the kinetic energy of flowing water into electricity, offering a continuous and reliable power source for farms and homesteads.
- Water flows through a turbine, causing it to spin and generate mechanical energy.
- This mechanical energy is converted into electricity via a generator.
- Excess energy can be stored in batteries or sold back to the grid in grid-tied systems.
Advantages of Small-Scale Hydropower
Small-scale hydropower systems are a game-changer for self-sufficient living, offering a stable energy source with minimal environmental impact. These systems are particularly valuable in areas with consistent water flow, providing an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to fossil fuels. Hydropower offers unique advantages compared to other renewable energy sources. Its ability to deliver consistent power regardless of weather conditions makes it a valuable addition to self-sufficient energy systems.
- Consistent Energy Supply: Unlike solar and wind power, hydropower provides a steady source of energy, day and night, year-round.
- Low Operating Costs: Once installed, small-scale turbines require minimal maintenance and have low operational expenses.
- Eco-Friendly: Hydropower systems produce zero emissions and have a smaller environmental footprint compared to large dams.
- Scalable: Systems can be customized for personal or agricultural energy needs, making them adaptable for various setups.
DIY Projects for Hydropower
DIY hydropower projects provide an accessible way for farms and homesteads to generate renewable energy on a budget. These small-scale solutions can be customized to suit individual needs, making them an excellent option for those seeking energy independence. Building your own hydropower system can be an affordable and practical way to harness water energy. With the right tools and resources, even small-scale projects can significantly reduce energy costs.
- DIY Micro-Hydro Systems: Use readily available kits to build small-scale systems for homes or farms. Recommended Resource: [DIY Micro-Hydro Kits Affiliate Links].
- Waterwheel Generators: Simple designs using a waterwheel and alternator can power small devices. Recommended Resource: [Waterwheel Generator Kits Affiliate Links].
Steps to Install a Small-Scale Hydropower System
Installing a small-scale hydropower system is a practical and rewarding way to harness renewable energy. With proper planning and execution, these systems can provide consistent and affordable power for homes and agricultural operations. Installing a small-scale hydropower system requires careful planning and execution. Following these steps ensures an efficient and sustainable energy solution tailored to your needs.
Site Assessment Evaluate your water source to determine its suitability for hydropower generation. Factors such as flow rate and vertical drop (head) are critical for calculating energy potential.
- Identify water sources with sufficient flow and head (vertical drop) to generate energy.
- Use tools like flow meters or [Water Flow Measurement Tools Affiliate Links] to measure water velocity and volume.
System Design A well-designed system maximizes energy production and ensures longevity.
- Calculate the energy potential based on water flow and head height.
- Choose a turbine type, such as Pelton, Kaplan, or cross-flow, depending on site conditions.
Selecting Components Choosing the right components ensures optimal system performance and durability.
- Turbine: Converts water flow into mechanical energy.
- Generator: Converts mechanical energy into electricity.
- Inverters and Batteries: Optional components for storing energy or converting it for grid use.
Installation Process Proper installation is essential for safety and efficiency.
- Install intake structures to channel water to the turbine.
- Set up the turbine and generator securely, ensuring proper alignment.
- Connect electrical components and test system performance.
Maintenance and Monitoring Regular maintenance ensures consistent energy production and system longevity.
- Regularly inspect the system for debris or blockages.
- Monitor performance using apps or sensors like [Energy Monitoring Systems Affiliate Links] to ensure consistent energy production.
Applications of Hydropower in Agriculture
Hydropower is a versatile energy source with numerous applications in agriculture. From powering irrigation pumps to running cold storage facilities, these systems play a critical role in reducing costs and increasing operational efficiency on farms. Hydropower systems are highly versatile, supporting various agricultural operations and reducing energy costs.
- Irrigation Pumps: Power water pumps to support efficient irrigation systems.
- Cold Storage: Operate refrigerators and freezers for perishable goods.
- Lighting and Heating: Illuminate barns and greenhouses or power heating systems.
- Small Machinery: Run equipment like grinders or saws used in farming operations.
Economic Considerations
Hydropower systems offer long-term financial benefits, making them a smart investment for farms and homesteads. Although initial installation costs can be significant, the low operational expenses and availability of incentives make these systems an economically viable option. Small-scale hydropower systems are cost-effective in the long run, offering significant savings and incentives.
- Installation Costs: Systems typically range from $1,500 to $10,000 depending on size and complexity.
- Operational Costs: Maintenance expenses are generally low, with periodic cleaning and part replacement.
- Financial Incentives: Explore tax rebates, grants, or subsidies for renewable energy projects to offset initial costs.
Environmental Benefits and Challenges
Hydropower systems offer substantial environmental benefits, including zero emissions and support for biodiversity. However, challenges such as sediment build-up and potential impacts on aquatic ecosystems require thoughtful design and proactive management to ensure sustainability. Hydropower systems align with sustainability goals by minimizing environmental impact, offering a clean and renewable energy source that reduces dependency on fossil fuels. These systems contribute to environmental preservation by producing zero emissions and supporting biodiversity. However, certain challenges, such as sediment build-up and potential effects on aquatic ecosystems, require proactive solutions and careful planning to maintain efficiency and ecological balance.
- Carbon Emission Reduction: Hydropower systems produce zero emissions, making them a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
- Sediment Build-Up: Address potential issues with sediment traps or periodic dredging to maintain water flow and system efficiency.
- Aquatic Ecosystems: Use fish-friendly turbines and properly designed intake structures to minimize ecological disruption.
Energy Storage Solutions
Energy storage solutions are essential for maintaining consistent power supply in hydropower systems. Properly storing energy ensures reliability during periods of low water flow, making it a critical component of any self-sufficient energy setup. Storing energy from hydropower systems ensures consistent supply during periods of low water flow or peak demand. Proper storage ensures energy reliability while protecting sensitive equipment and systems.
- Battery Types: Lithium-ion batteries are ideal for small-scale systems due to their efficiency, longevity, and energy density. These batteries should be stored in cool, dry, and well-ventilated areas such as a dedicated utility room or shed. For larger systems, consider building a separate insulated and ventilated structure to house battery banks and related components safely.
- Pumped-Storage Systems: Excess energy can be used to pump water to an elevated reservoir, storing it for future energy production during peak demand. This solution is particularly effective for farms with suitable land elevation and water flow conditions.
Practical Examples of Integration
Integrating hydropower with other renewable energy sources creates a robust and versatile energy system. By combining technologies like solar panels and wind turbines, farms and homesteads can achieve greater energy independence and efficiency. Integrating hydropower with other renewable energy sources creates hybrid systems that maximize energy production and reliability.
- Hybrid Systems: Combine hydropower with solar panels or wind turbines to ensure consistent energy production during seasonal water flow variations.
- Grid-Tied Options: Sell surplus energy to local utilities for additional income or energy credits.
Transform Your Farm or Homestead with Hydropower
Hydropower offers farms and homesteads an efficient and eco-friendly energy solution that supports sustainability and resilience. With tools like [DIY Micro-Hydro Kits Affiliate Links] and [Fish-Friendly Turbine Kits Affiliate Links], integrating hydropower into your energy plan is more accessible than ever. Embrace hydropower to achieve energy independence and create a sustainable future for your farm or homestead.
Biogas Plants: Generating Energy from Organic Waste and Livestock Manure
Biogas plants are a cornerstone of sustainable energy systems, providing an innovative way to transform waste into valuable resources. By converting organic materials like livestock manure, food waste, and agricultural residues into methane gas, these systems offer reliable energy solutions for cooking, heating, and electricity generation. Beyond energy production, biogas plants contribute to environmental conservation by reducing waste and producing digestate, a nutrient-rich fertilizer that supports sustainable agriculture. These systems empower farms and homesteads to embrace energy independence while addressing waste management challenges.
How Biogas Plants Work
Biogas plants operate through a process called anaerobic digestion, where microorganisms break down organic waste in the absence of oxygen. This process generates methane gas, which can be captured and used as a versatile energy source. Alongside energy production, these systems create digestate, a byproduct rich in nutrients, that serves as an organic fertilizer, supporting sustainable agriculture.
- Organic waste, such as manure and crop residues, is collected and fed into the digester.
- Inside the digester, anaerobic bacteria break down the waste to produce biogas (a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide).
- The methane is captured and stored in gas holders for later use in cooking, heating, or electricity generation.
- The remaining material is processed into digestate for use as fertilizer.
Advantages of Biogas Systems
Biogas systems offer multiple benefits for farms and homesteads, addressing both energy needs and waste management challenges. These systems create a circular economy by transforming organic waste into valuable resources.
- Renewable Energy Source: Converts organic waste into a sustainable and locally available energy supply.
- Waste Management: Reduces environmental impact by diverting waste from landfills and waterways.
- Cost Savings: Lowers energy expenses and reduces dependency on fossil fuels.
- Fertilizer Production: Produces nutrient-rich digestate that improves soil health and crop yields.
- Carbon Emission Reduction: Captures methane emissions from decomposing waste, mitigating climate change.
Steps to Set Up a Biogas Plant
Setting up a biogas plant involves careful planning and consideration of site-specific factors. By following these steps, you can ensure a successful and efficient system tailored to your energy and agricultural needs.
Determine Feasibility Start by assessing the availability of organic waste and evaluating your energy requirements. Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to ensure the project’s viability.
- Calculate daily waste production, considering livestock manure, crop residues, and food scraps.
- Estimate the energy output based on waste volume and system capacity.
Choose the Right System Select a biogas plant design that aligns with your scale and type of waste.
- Fixed-Dome Plants: Ideal for small-scale farms and households.
- Floating-Dome Plants: Suitable for medium-scale operations with variable gas production.
- Plug-Flow Digesters: Best for liquid waste with high manure content.
Construction and Installation Proper installation is critical for maximizing system efficiency and safety.
- Install the digester, gas storage unit, and pipelines for gas transfer.
- Ensure insulation to maintain optimal digestion temperatures.
- Use tools like [Biogas Digester Kits Affiliate Links] to streamline construction.
Operation and Maintenance Regular maintenance ensures consistent performance and longevity.
- Feed the digester with organic material on a daily or weekly schedule.
- Monitor gas production using sensors like [Monitoring Sensors Affiliate Links].
- Inspect and clean components periodically to prevent blockages or leaks.
Livestock and Biogas Integration
Livestock farms are uniquely positioned to benefit from biogas systems, as they offer a consistent source of organic waste while addressing key environmental and operational challenges. These systems efficiently convert manure into renewable energy, reducing waste management costs and improving overall farm hygiene. Heat generated during biogas combustion can also be used to warm livestock shelters, enhancing animal welfare during colder months. By integrating digesters near barns, farmers can simplify manure collection and create a seamless system that optimizes both energy production and waste reduction.
Applications of Biogas in Agriculture
Biogas systems unlock numerous opportunities for farms and homesteads, from powering daily operations to reducing environmental impact.
- Cooking and Heating: Power stoves, water heaters, and farm buildings.
- Electricity Generation: Operate generators to supply power to farms or sell back to the grid.
- Machinery Fuel: Run biogas-compatible tractors or small farming equipment.
- Wastewater Treatment: Process slurry from livestock or crop washing stations.
What Can You Utilize in a Biogas Plant?
A wide variety of organic materials can fuel biogas systems, making them versatile and scalable solutions for farms of all sizes.
- Livestock Manure: High-yield inputs such as cow, pig, and chicken manure.
- Crop Residues: Corn stalks, wheat straw, and other agricultural byproducts.
- Food Waste: Kitchen scraps, spoiled produce, and dairy waste.
- Grass Clippings and Leaves: Adds bulk to the digester and improves biogas output.
- Aquatic Plants: Fast-growing plants like duckweed and water hyacinth can also be digested.
When Is a Biogas Plant Worthwhile?
The feasibility of a biogas plant is influenced by factors such as waste availability, energy requirements, and space constraints. Small-scale systems are ideal for farms producing 5–15 kg of waste daily, requiring 50–100 square meters of space. Medium-scale systems, accommodating larger operations, may need up to 500 square meters. Rural areas with consistent organic waste sources, such as livestock farms or food processing facilities, are especially suitable. Return on investment is enhanced through government incentives, reduced energy costs, and the sale of surplus digestate or energy to nearby communities.
Costs and Ways to Save Money
The initial costs of biogas systems can vary depending on their size and complexity, but with proper planning, they can become a cost-effective investment. Farms and homesteads can take advantage of financial incentives and creative solutions to offset upfront expenses.
Installation Costs Small-scale systems typically cost between $3,000 and $10,000, while medium-scale operations may range from $10,000 to $50,000. These costs include the digester, gas storage, and installation labor.
- Grants and Subsidies: Many governments and organizations offer financial assistance to support renewable energy projects.
- DIY Kits: Using affordable [DIY Biogas Kits Affiliate Links] can significantly reduce initial setup costs for small systems.
- Community Collaboration: Neighboring farms can pool resources to establish shared biogas plants, reducing individual expenses.
- Repurposing Infrastructure: Repurposing existing tanks or pipelines can lower setup costs while maintaining efficiency.
- Selling Surplus Energy: Grid-tied systems allow farms to sell excess energy, generating an additional income stream.
Transform Your Waste into Energy
Biogas systems offer a powerful way to transform organic waste into renewable energy, creating a sustainable and cost-effective solution for farms and homesteads. With tools like [Biogas Digester Kits Affiliate Links] and [Monitoring Sensors Affiliate Links], adopting biogas technology is simpler than ever. Start your journey today to achieve energy independence and environmental sustainability.
Wind Power: Harnessing the Wind for Sustainable Energy
Wind power is a reliable and efficient source of renewable energy, offering an excellent solution for farms and homesteads located in areas with consistent wind. By harnessing the power of natural breezes, wind turbines generate electricity that can power homes, machinery, and agricultural operations. This clean and sustainable energy source contributes to energy independence while reducing environmental impact.
How Wind Power Works
Wind turbines capture kinetic energy from the wind and convert it into mechanical energy. This energy is then transformed into electricity through a generator. Modern small-scale turbines are designed to be efficient and adaptable, making them suitable for a variety of applications, from powering irrigation pumps to supporting hybrid energy systems.
- Key Components: Wind turbines include blades, a rotor, a generator, and a tower to elevate the system for maximum wind exposure.
- Energy Conversion: As wind rotates the blades, the rotor turns a shaft connected to a generator, producing electricity.
- Scalability: Systems can be tailored for personal or agricultural energy needs.
Advantages of Wind Power
- Reliable Energy Source: Ideal for areas with steady wind, providing consistent power generation.
- Low Operational Costs: Once installed, wind turbines require minimal maintenance and no fuel.
- Environmental Benefits: Produces zero emissions, supporting climate goals and sustainability.
- Versatility: Can be used as a standalone system or part of a hybrid renewable energy setup.
Steps to Install a Small-Scale Wind System
Installing a wind turbine involves careful planning and execution to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Site Assessment Evaluate your property’s wind conditions to determine the feasibility of installing a wind turbine.
- Measure wind speed and consistency using anemometers or wind maps.
- Identify suitable locations with minimal obstructions to ensure maximum wind capture.
System Design Tailor the wind turbine system to your specific energy needs and site conditions.
- Choose a turbine size based on energy requirements and wind availability.
- Decide between grid-tied or off-grid systems depending on your goals.
Installation Proper installation is critical for safety and efficiency.
- Select a tower height that maximizes wind exposure.
- Ensure proper anchoring and grounding for stability.
- Use professional services or follow detailed guides for installation.
Monitoring and Maintenance Routine maintenance ensures consistent performance and system longevity.
- Inspect blades, bearings, and connections regularly.
- Monitor energy output with tools like Energy Monitoring Systems Affiliate Links to track performance and identify issues early.
Applications of Wind Power in Agriculture
Wind power is highly versatile and supports various agricultural operations, reducing dependency on traditional energy sources.
- Irrigation Systems: Power water pumps for reliable and efficient irrigation.
- Cold Storage: Maintain refrigeration units for perishable goods.
- Lighting and Heating: Illuminate barns and greenhouses or power heating systems.
- Small Machinery: Operate equipment such as grinders or saws used in farming.
Challenges and Solutions
While wind power offers numerous benefits, it also comes with challenges that require proactive solutions.
- Noise and Aesthetics: Modern, low-noise turbine models help mitigate sound concerns, while thoughtful placement away from living areas minimizes visual disruption.
- Wildlife Impact: Bird-safe turbine designs, such as slower-rotating blades and ultrasonic deterrents, reduce risks to local wildlife. Situating turbines away from migratory paths further minimizes harm.
- Initial Costs: Installing a small-scale wind turbine system can cost between $10,000 and $50,000, depending on turbine size and site conditions. Larger farm-scale systems may exceed $100,000. However, these costs can be offset through government incentives, grants, and cooperative initiatives. Additionally, farms often recoup their investment within 5–10 years due to energy savings and revenue from selling surplus electricity.
- Legal and Zoning Requirements: Farmers should consult local regulations to ensure compliance with height restrictions and permitting processes. Professional services can streamline this aspect of planning. Many farms also benefit from leasing turbine space to energy companies, creating an additional income stream.
- Legal and Zoning Requirements: Farmers should consult local regulations to ensure compliance with height restrictions and permitting processes. Professional services can streamline this aspect of planning.
Case Studies
Denmark: Small farms in Denmark use wind turbines to power dairy operations and irrigation systems, achieving energy independence while selling surplus electricity back to the grid. Farmers report saving 30% on operational costs annually.
United States: A homestead in Kansas combines wind turbines with solar panels, creating a hybrid system that powers all farm operations year-round. This setup reduces energy expenses by approximately $5,000 annually while ensuring reliability during storms.
Germany: Wind turbines on rural farms supplement solar systems during cloudy months, ensuring consistent energy supply for greenhouses and storage facilities. Many farms reinvest profits from surplus energy sales into expanding their renewable systems.
Kenya: Community farms in Kenya integrate wind turbines with biogas systems, powering irrigation pumps and storage facilities. This hybrid approach has improved agricultural productivity by 40% and reduced reliance on diesel generators.
Imagine standing in a field where the gentle hum of wind turbines accompanies the breeze, knowing your farm or homestead is powered by clean, renewable energy. Wind power is more than an energy source—it is a pathway to freedom from utility bills, enhanced sustainability, and self-reliance.
Although initial investments for wind turbines may seem high, the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. With potential energy savings of $3,000–$10,000 annually for small-scale systems and even greater returns for larger operations, wind power is both an economically viable and environmentally friendly choice. Farmers and homesteaders leveraging government incentives and energy sales often recoup their investments within a few years, making it a transformative addition to any renewable energy setup.
By adopting wind power, you can reduce operational costs, lower your environmental footprint, and achieve energy independence. Whether you’re powering irrigation, heating greenhouses, or supporting hybrid energy systems, wind turbines offer a practical and efficient solution for modern self-sufficient living. Begin exploring wind power today and unlock the transformative potential of this renewable energy source for your farm, homestead, or community.
Integrating Renewable Energy into Sustainable Farming Systems
Renewable energy is at the heart of sustainable farming, providing farmers with reliable, cost-effective, and eco-friendly power solutions. By integrating renewable energy systems such as solar, wind, hydropower, and biogas, farms can effectively reduce costs and improve resilience. These systems offer farmers the tools to operate sustainably while maintaining high levels of productivity and addressing energy challenges head-on. Integration also fosters financial independence, operational reliability, and greater environmental stewardship for farmers worldwide.
The Role of Renewable Energy in Farming
Renewable energy has transformed the way farms operate by introducing clean and reliable power solutions. By reducing dependency on fossil fuels and lowering operational costs, these systems empower farmers to enhance productivity while supporting global sustainability goals. For instance, scalable Solar Panel Kits can power irrigation systems and cold storage units, offering versatile and renewable solutions tailored to varying farm needs. Meanwhile, Wind Turbine Systems complement solar setups in regions with consistent wind resources, ensuring energy reliability. Farms with organic waste can utilize Biogas Systems to generate clean energy while managing waste effectively. This integration ensures consistent energy availability, supporting farms during extreme weather events or grid outages, making renewable systems indispensable to modern agriculture.
Key Strategies for Integration
Implementing renewable energy systems on farms requires strategic planning and optimization to ensure maximum efficiency and output. By combining multiple energy sources and leveraging smart technologies, farmers can create versatile and resilient operations.
Combining Energy Sources Farms can achieve consistent energy production by combining renewable systems tailored to their specific needs. Pairing Solar Panel Kits with Wind Turbine Systems ensures reliable energy in diverse weather conditions, while Biogas Systems serve as a dependable backup during periods of low solar or wind output. Additionally, Hydropower Turbine Kits can harness water resources to generate sustainable energy, creating hybrid systems that enhance efficiency and resilience.
Battery Storage and Management Storing excess energy is crucial for maintaining energy reliability during peak demand or low production times. High-capacity battery storage systems, like those found in Battery Storage Solutions, are essential for capturing and storing surplus energy for later use. These systems help farms maintain consistent power supply during peak demand or low production times. Using tools like Energy Monitoring Systems, farmers can optimize energy storage efficiency while ensuring their renewable energy investments provide long-term value.
- Install high-capacity energy storage systems to capture surplus energy for later use.
- Use tools like [Battery Storage Solutions Affiliate Links] to select efficient and durable battery options.
Optimizing Land Use Maximizing land productivity while integrating renewable energy systems is essential for efficient operations.
- Implement agrivoltaics by installing solar panels above crops, creating microclimates that enhance plant growth.
- Use underutilized areas near barns or water sources for hydropower or biogas installations, ensuring land efficiency.
Smart Monitoring Systems Modern farms benefit from integrating smart technologies to monitor and optimize energy production and consumption. Tools like Energy Monitoring Systems provide real-time data on performance, enabling farmers to identify inefficiencies and ensure peak efficiency. By combining IoT and AI tools, farms can automate energy usage, reduce waste, and improve overall system reliability.
Examples of Renewable Energy Integration
Real-world examples highlight how renewable energy transforms agricultural operations globally. In India, Solar Panel Kits power irrigation systems and Biogas Systems support clean cooking, reducing dependence on fossil fuels. Germany showcases hybrid systems with Wind Turbine Systems and solar arrays powering refrigeration units and irrigation pumps year-round. In the U.S., a vineyard integrates Hydropower Turbine Kits for irrigation while using agrivoltaics to improve crop quality. Similarly, smallholder farms in Kenya use compact Biogas Systems to convert waste into energy, creating cost-effective and sustainable solutions for rural communities.
Benefits of Integrating Renewable Energy
Integrating renewable energy systems into farming operations offers a transformative opportunity to enhance sustainability, resilience, and cost savings. By adopting solutions like solar panels, biogas systems, and hydropower, farmers can achieve long-term energy independence and contribute to environmental conservation. Combining modern tools such as Energy Monitoring Systems and Battery Storage Solutions ensures that farms operate efficiently while maximizing resource utilization. These systems not only reduce energy bills but also strengthen farming operations against power outages and climate challenges. Start your renewable energy journey today and unlock the potential of a future-ready, eco-friendly farm that thrives in any conditions.
Case Studies of Farms and Communities Using Alternative Energy Sources
Renewable energy systems have been successfully integrated into various farming operations and communities worldwide, showcasing their adaptability and transformative potential. These systems not only reduce costs and improve productivity but also contribute to environmental conservation. Below are detailed examples highlighting how farms and communities are harnessing renewable energy to enhance efficiency and sustainability.
In Rajasthan, India, farms use solar panels to power water pumps and biogas systems for cooking, replacing the reliance on diesel engines and firewood. This shift has significantly reduced energy costs and improved reliability in remote areas, while financial incentives from local governments have accelerated the adoption of these systems. Farmers report increased productivity and reduced environmental impact, demonstrating the effectiveness of renewable integration.
In Bavaria, Germany, small-scale hybrid farms combine wind turbines and solar arrays to power irrigation pumps, refrigeration units, and milking machines. These farms have achieved complete energy independence, with many selling surplus energy back to the grid. This dual benefit of energy security and additional income has made renewable energy an attractive option for small-scale farmers across the region.
In Kenya, community farming projects in rural areas rely on solar and biogas systems to power irrigation and provide clean cooking gas. These renewable energy solutions have boosted agricultural productivity while significantly reducing deforestation and the dependence on charcoal. Additionally, solar-powered lighting systems have improved safety and efficiency during nighttime farming activities.
In the United States, renewable energy integration showcases remarkable versatility. A vineyard in California combines hydropower for irrigation with agrivoltaics to shade vines, reducing water evaporation and enhancing grape quality. Meanwhile, a family farm in Colorado employs a hybrid system of wind turbines, solar panels, and a micro-hydro setup to power all operations, achieving 100% energy independence. These examples highlight how diverse renewable energy systems can adapt to different agricultural needs.
In the Netherlands, advanced greenhouses incorporate geothermal heating and solar panels to support year-round crop production. The surplus energy generated by solar panels is sold to nearby households, creating an additional income stream for farmers. This integration of renewable energy has revolutionized greenhouse operations, ensuring sustainability and profitability for local agricultural businesses.
In Nepal, micro-hydro projects supply reliable electricity to smallholder farms and rural communities. These systems power irrigation pumps, grain mills, and lighting, greatly improving agricultural efficiency while reducing the burden of manual labor. Communities benefiting from micro-hydro projects have reported higher crop yields and improved living standards, showcasing the profound impact of renewable energy solutions in remote areas.
In São Paulo, Brazil, cattle farms utilize biogas systems to process livestock manure, generating clean electricity for daily operations and producing nutrient-rich digestate as fertilizer. Surplus electricity is sold back to the grid, creating an additional revenue stream for farmers. This circular approach addresses waste management while boosting energy efficiency, setting a sustainable standard for modern livestock farming.
In Australia, remote cattle stations in Queensland leverage solar panels and wind turbines to power water pumps, refrigeration units, and communication systems. These renewable energy systems have significantly reduced reliance on diesel fuel, cutting costs and emissions. Additionally, the enhanced operational resilience ensures that farms remain productive even during extreme weather conditions, further proving the reliability of renewable energy.
In South Africa, vineyards in the Western Cape employ floating solar panels installed on farm dams. This innovative approach not only generates electricity for irrigation and cold storage systems but also reduces water evaporation, a critical advantage in regions prone to drought. Farmers have seen increased energy savings and water conservation, making floating solar panels a practical and sustainable solution.
In Provence, France, an organic farm integrates solar panels and biogas systems to power cold storage units and greenhouses. This dual-energy approach significantly reduces energy costs while supporting the farm’s sustainability goals. The use of digestate from biogas production further enhances soil health, completing the cycle of renewable energy and sustainable farming.
Renewable energy systems have proven to be transformative in farming and community development, offering unparalleled opportunities for sustainability, cost savings, and resilience. These solutions showcase the potential to revolutionize agriculture while addressing environmental challenges and ensuring energy independence. By adopting renewable energy technologies, farmers and communities are building a future where productivity and environmental harmony coexist seamlessly.
Whether it’s solar-powered irrigation in India, floating solar panels in South Africa, or hybrid systems in Germany, these examples highlight the versatility and effectiveness of renewable energy systems in diverse contexts. Explore these solutions today to unlock the potential of renewable energy and create a more sustainable and resilient future for your farm or community.
Tools, Resources, and Guides for Setting Up Energy-Efficient Systems
Integrating renewable energy systems into your farm or homestead is easier than ever with the right tools and resources. These solutions provide everything from power generation to storage and monitoring, empowering individuals to create sustainable, self-sufficient systems that cater to their unique needs. Below is a comprehensive guide to tools and resources that simplify the process of setting up energy-efficient systems.
Renewable Energy Starter Kits
Renewable energy starter kits are perfect for beginners looking to dive into energy-efficient living. These bundled systems include solar panels, batteries, and inverters, providing everything needed to generate and store energy. Starter kits simplify the setup process, making them ideal for those with minimal experience in renewable energy systems.
- Applications: Powering homes, small farms, or off-grid cabins.
- Recommended Resource: [Renewable Starter Kits Affiliate Links].
Solar Water Pump Systems
Solar water pump systems are an essential tool for off-grid farms and homesteads. By harnessing solar energy, these systems provide reliable irrigation without relying on fossil fuels or external electricity sources. They are especially beneficial in regions with abundant sunlight and limited water access.
- Applications: Irrigating crops, watering livestock, and supplying water to remote areas.
- Recommended Resource: [Solar Water Pump Kits Affiliate Links].
Wind and Solar Hybrid Systems
Combining wind turbines with solar panels, hybrid systems maximize energy production regardless of weather conditions. These systems are highly versatile and adaptable to various climates, making them an excellent choice for farms looking to achieve year-round energy stability.
- Applications: Providing consistent energy for farms in areas with both wind and sunlight.
- Recommended Resource: [Hybrid Energy Systems Affiliate Links].
Thermal Energy Storage Systems
Thermal energy storage systems capture and store heat for later use, making them ideal for greenhouses and farm heating systems. These systems enhance energy efficiency by reducing dependency on traditional heating methods and lowering operational costs.
- Applications: Heating greenhouses, water systems, or farm buildings.
- Recommended Resource: [Thermal Energy Storage Solutions Affiliate Links].
Portable Solar Chargers
Portable solar chargers are compact, mobile solutions for powering small tools and devices. These chargers are perfect for farmers who need portable energy sources for fieldwork or small-scale equipment.
- Applications: Charging mobile devices, electric tools, or monitoring equipment in remote locations.
- Recommended Resource: [Portable Solar Charger Kits Affiliate Links].
Composting Heat Recovery Systems
Composting heat recovery systems convert the natural heat generated by composting organic materials into usable energy. These systems are an innovative way to reduce waste and power small-scale heating needs on farms.
- Applications: Heating water or farm buildings using compost heat.
- Recommended Resource: [Composting Heat Systems Affiliate Links].
Geothermal Heating Solutions
Geothermal heating systems are highly effective for year-round climate control in greenhouses and farm buildings. By tapping into the earth’s consistent underground temperatures, these systems provide efficient and sustainable heating solutions.
- Applications: Climate control in greenhouses or livestock shelters.
- Recommended Resource: [Geothermal Heating Systems Affiliate Links].
Energy Assessment Tools
Energy assessment tools help farmers evaluate their energy needs and identify the most suitable renewable energy solutions. These tools, which can be used online or with professional services, are invaluable for planning efficient systems tailored to specific requirements.
- Applications: Conducting energy audits to optimize system design.
- Recommended Resource: [Energy Audit Services Affiliate Links].
Solar Panel Kits
Solar panel kits are a cornerstone of renewable energy systems, offering reliable and scalable solutions for energy production. These kits are ideal for farms and homesteads aiming to harness the power of the sun for sustainable living.
- Applications: Powering irrigation systems, greenhouses, and household appliances.
- Recommended Resource: [Solar Panel Kits Affiliate Links].
Wind Turbine Systems
Wind turbine systems provide cost-effective energy solutions for farms located in windy regions. These systems are particularly effective as part of hybrid setups, ensuring energy production during periods of low sunlight.
- Applications: Powering farm operations, irrigation systems, and storage facilities.
- Recommended Resource: [Wind Turbine Systems Affiliate Links].
Biogas Digesters
Biogas digesters are an efficient way to convert organic waste into renewable energy. These systems produce biogas for cooking or heating while generating nutrient-rich fertilizer as a byproduct, making them a valuable addition to farms.
- Applications: Managing organic waste and producing energy for daily farm operations.
- Recommended Resource: [Biogas Plant Kits Affiliate Links].
Hydropower Turbines
Hydropower turbines harness the energy of flowing water to generate electricity, offering a reliable energy solution for farms with access to streams or rivers. These systems are ideal for powering water pumps and small machinery.
- Applications: Generating electricity for irrigation and farm equipment.
- Recommended Resource: [Hydropower Turbine Kits Affiliate Links].
Battery Storage Systems
Battery storage systems are critical for storing surplus energy and ensuring consistent power supply during periods of low energy production. These systems maximize the efficiency of renewable energy setups, making them an essential component for farms.
- Applications: Storing energy for nighttime use or during cloudy weather.
- Recommended Resource: [Battery Storage Solutions Affiliate Links].
IoT Monitoring Tools
IoT monitoring tools enable farmers to track and manage their energy production and consumption in real time. These tools optimize energy usage and ensure that renewable systems operate at peak efficiency.
- Applications: Monitoring renewable energy systems to identify inefficiencies and improve performance.
- Recommended Resource: [Energy Monitoring Systems Affiliate Links].
Transform Your Farm or Homestead with the Right Tools
The right tools and resources are key to creating energy-efficient, sustainable systems that transform your farm or homestead. From solar panel kits to IoT monitoring tools, these solutions simplify the integration of renewable energy systems, empowering you to achieve energy independence and sustainability. Explore these tools today and take the first step toward a self-sufficient future.
Suggested Reading, Workshops, and Resources
Recommended Tools and Resources
• [Solar Panel Kits Affiliate Links]: Efficient photovoltaic systems for diverse farming needs.
• [Biogas Plant Kits Affiliate Links]: Turn organic waste into renewable energy.
• [Hydropower Turbine Kits Affiliate Links]: Reliable turbines for water-based energy production.
• [Wind Turbine Systems Affiliate Links]: Cost-effective wind energy solutions for farms.
• [Geothermal Heating Systems Affiliate Links]: Ideal for greenhouses and year-round farming.
• [Floating Solar Kits Affiliate Links]: Innovative solutions for water and energy efficiency.
Recommended Books
- Renewable Energy for Dummies by Rik DeGunther: A beginner-friendly overview of renewable energy systems.
- The Homeowner’s Guide to Renewable Energy by Dan Chiras: Practical advice for setting up energy systems at home or on farms.
• The Renewable Energy Handbook by William Kemp.
• Biogas for Rural Communities by Rao Y. Surampalli.
• The Solar Economy by Hermann Scheer.
• Wind Power Basics by Dan Chiras.
• Power from the Sun by Dan Halacy.
• Viktor Schauberger: A Life of Learning from Nature by Jane Cobbald.
• The Energy Evolution: Harnessing Free Energy from Nature by Viktor Schauberger.
• Living Energies by Callum Coats (based on Schauberger’s work).
• Tesla: Inventor of the Modern by Richard Munson.
• My Inventions: The Autobiography of Nikola Tesla by Nikola Tesla.
Workshops
- Local sustainable farming workshops integrating renewable energy (check with regional agricultural organizations).
- Government-funded renewable energy project webinars (specific to your region).
Additional Recommendations
Videos
- How Renewable Energy Works (YouTube series): Detailed walkthroughs on renewable systems like solar, wind, and biogas.
- Earthships: Off-Grid Living Documentary: Highlights renewable integration in self-sufficient homes.
• The Secret of Water (Documentary on Schauberger’s theories).
• Educational content on renewable energy from channels like Fully Charged Show or Undecided with Matt Ferrell.
Courses
- Earthship Biotecture Academy: Hands-on training for off-grid, renewable energy housing.
- Green Building and Energy Systems by Coursera: Comprehensive online course focusing on energy-efficient design.
• Introduction to Renewable Energy by Solar Energy International (SEI).
• Permaculture and Renewable Energy Integration workshops (available through local permaculture centers).
Audiobooks
- The Solar Revolution: The Economic Transformation of the Global Energy Industry by Travis Bradford: Explains the global shift toward solar power.
- Wind Power for Dummies: Covers basic to advanced wind turbine systems.
• Tesla: Inventor of the Modern (Audiobook version).
• The Water Wizard: The Extraordinary Properties of Natural Water by Viktor Schauberger, narrated in audiobook format.
Recommendations
Combining renewable energy systems is a key strategy for achieving energy independence and sustainability on farms and homesteads. Below are actionable recommendations for maximizing the benefits of renewable energy integration:
- Combine renewable systems: Pair solar panels with biogas or wind turbines to create a balanced and reliable energy supply that adapts to varying weather conditions.
- Leverage financial incentives: Take advantage of government grants, tax incentives, and subsidies to reduce installation costs and improve return on investment.
- Use IoT tools for monitoring: Regularly monitor and maintain systems with IoT-enabled tools to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Explore hybrid setups: Consider hybrid systems, such as combining solar and biogas, to enhance energy reliability and maximize efficiency.
- Engage in education: Attend workshops, enroll in courses, and visit successful renewable energy projects to gain practical knowledge and inspiration.
Key Points
- Integrating renewable energy systems reduces costs, enhances sustainability, and supports energy independence.
- Tools like biogas digesters, solar panels, and wind turbines provide scalable solutions for farms and homesteads.
- Hybrid systems maximize energy production, ensuring resilience during varying weather conditions.
- Practical resources like online tools, books, and workshops make renewable systems accessible for beginners and experts alike.
- Visiting farms that have successfully implemented renewable energy systems offers real-world insights and valuable lessons.
Conclusion
Imagine powering your home with the energy of the sun, free from utility bills and full of independence. Renewable energy systems offer far more than just financial savings—they provide a lifestyle rooted in sustainability, resilience, and self-sufficiency. From solar panels and wind turbines to biogas digesters and hydropower, these technologies are fundamentally transforming the way we power our homes, farms, and communities.
Adopting renewable energy systems is not just a choice; it is a commitment to a sustainable and resilient future. With solar panels generating clean electricity, wind turbines harnessing natural breezes, and biogas systems turning waste into energy, the opportunities are endless. These solutions reduce environmental impact, cut energy costs, and ensure reliable power, even in remote or off-grid locations.
Picture your farm or homestead thriving with renewable systems—irrigation powered by the sun, buildings heated through geothermal energy, and excess electricity stored for future use. Whether you’re starting small or embarking on a large-scale system, renewable energy opens the door to independence and environmental harmony. Now is the time to explore these transformative solutions and create a self-sufficient, sustainable future for yourself and your community.
FAQ
What are the best renewable energy systems for farms and homesteads?
The best systems depend on your location and needs. Solar panels, biogas digesters, wind turbines, and hydropower systems are all excellent options, often used in combination for maximum efficiency.
How much does it cost to install a renewable energy system?
Costs vary based on the system size and type. Small systems may cost $3,000–$10,000, while larger setups can exceed $50,000. Government incentives and subsidies can significantly offset these costs.
Can I integrate renewable energy into my existing farm?
Yes, renewable systems like solar panels, wind turbines, and biogas digesters can be retrofitted into most farms and homesteads. Consulting with experts or using online tools can help with planning and integration.
What maintenance is required for renewable energy systems?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning solar panels, inspecting turbines, and monitoring biogas digesters for blockages. IoT tools can help track performance and alert you to potential issues.
Are there government programs to support renewable energy adoption?
Many governments offer grants, tax rebates, and subsidies to encourage renewable energy use. Check with local agencies for programs available in your area.
How do hybrid systems work?
Hybrid systems combine two or more energy sources, such as solar and wind, to ensure consistent energy production even during varying weather conditions.
What are the environmental benefits of renewable energy?
Renewable energy systems reduce greenhouse gas emissions, decrease reliance on fossil fuels, and promote sustainable resource use. They also improve local air and water quality.